https://medicinedepartment.blogspot.com/2021/10/mbbs-2017-batch-oct-2021-internal.html?m=1
1)Define Bone density,how it is measured?What are the causes,clinical features, diagnosis and management of Osteoporosis?
Bone density: It is a measure of the mineral content of bone .It is mostly calcium
It measures areal bone density (mineral/surface area).
It is usually measured by DEXA(Dual energy X-RAY absorptiometry).
2)What is Myxedema coma?Describe it's clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of Myxedema coma?
Myxedema coma is a life-threatening medical emergency with a high mortality rate that develops as a complication of severe hypothyroidism.
Hallmarks: Decreased mentation, hypothermia.
Treatment: Hypothyroidism: Initial i.v dose of 200-400mcgT4,followed by daily i.v dose of 50-100mcg until oral dose is possible.Total serum T4 should increase by 2-4mcg/DL.
I.v T3 intially 5-20mcg,followed by 2.5-10mcg
every 8hours.
Treatment of Hypertension:
Beta-adrenergic antagonists:atenolol,Timolol
Maelate,betaxolol,labetalol.
Atenolol-Initial dose of 50mg po daily.
ACE Inhibitors:captopril,enalapril(20mg daily), Lisinopril.
Angiotensin receptor blockers:Losaratan(50-100mg daily),candesartan,valsartan.
Calcium channel blockers:Nifedipine(10-20mg TlD (or)QID,Verapamil.
Diuretics:
Thiazides:Hydrochlorothiazide,chlorthalidone.
Loop diuretics: Furosemide,bumetanide.
Potassium sparing diuretics:Amiloride,Triamterene.
Direct renin inhibitor:Aliskiren
Alpha adrenergic antagonists: Doxazosin,prazosin,terazocin.
Centrally acting adrenergic agonists:
Clonidine,methyldopa.
Direct acting vasodilators: Hydralazine, Minoxidil.
7)What are the causes, pathogenesis and differential diagnosis of ascites?
8) Approach to Acute pancreatitis?
Cullen's sign: Faint bluish discoloration around umbilicus.
Peripheral blood picture:
Macro-Ovalocytes
Pancytopenia
Basophilic stippling,Cabot ring,Howell-jolly
Bodies.
Treatment:
Vitamin B12 therapy: Initial dose with six I.M injections of hydroxycobalamin 1,000mcg given at 3-7day intervals.
Maintenance dose:1,000mcg i.m every 3months for rest of patient's life.
Folate therapy:Oral dose of 5mg folate daily
for 3weeks and maintenance dose of 5mg
Once weekly.
5)Causes, diagnosis and treatment of atrial
Fibrillation?
Causes:
Cardiac:
Hypertensive heart disease
Valvular heart diseases(mitral stenosis)
Non cardiac:
Pneumonia,COPD, Pulmonary embolism,
Hyperthyroidism,Drugs and alcohol.
Diagnosis:
ECG Changes: No clear P waves,F waves.
Atrial rate:350-500bpm
Ventricular rate: irregularly irregular
2D Echo to look for LA Size,thrombus,LV Function.
Catheterization:Before ablation
Chest x-ray
Thyroid function tests and serum electrolytes.
Fasting lipid profile.
9) Mention the differences between in findings between UMN and LMN lesion?
UMN LESION:
Weakness; voluntary movements are disturbed; distal predominant
Tone; hypertonia( claspknife spasticity)
*Reflex (tendon); increased,
*Reflex (superficial); absent or decreased
Plantar response; extensor
*Muscle atrophy; disuse
*Fasciculations ; absent
*Bilateral movements; spared
(Eyes,face,jaw,neck)
*Reaction of degeneration; absent
* Nerve conduction; normal
LMN LESION:
Weakness; paralysis of muscles supplied by that segment or nerve proximalpredominant
Tone; hypotonia
Reflex (tendon); decreased or absent
*Reflex (superficial); absent or decreased
Plantar response; flexor or absent
*Muscle atrophy; marked
*Fasciculations ; often present
*Bilateral movements; affected
(Eyes,face,jaw,neck)
*Reaction of degeneration; present
* Nerve conduction; abnormal
10) INDICATION OF HEMODIALYSIS ?
Acute renal failure
✓Toxins , Poisoning
✓Drugs
✓Chronic renal failure patients awaiting renal transplantation
✓patients with CRF in whom quality of life has deteriorated
12) RENAL MANIFESTATIONS OF SNAKE BITE?
✓ Hematuria
✓Hemoglobinuria
✓Myoglobinuria
✓Loin pain
✓Renal failure
14)ans; Down's syndrome clinical features;
✓Craniofacial and musculoskeletal;
Flat nasal bridge,flat face,brachycephaly,malformed large ears,hypertelorism,slanting eyes with epicanthic folds, protruding furrowed tongue
Broad short neck,simian crease,short stature,hypotonia
Increased space b/w first and second toes(sandal gap)
✓Brain; increased frequency of sleep apnea syndrome,mental retardation,Adhd,autism
✓Heart; ASD,VSD,tetralogy of fallot
✓Git;. Oesophageal or duodenal atresia,imperforate anus
✓Reproductive;males are sterile
✓endocrine; Hypothyroidism,type-1DM
✓Bone marrow; increased incidence of acute leukemia
16ans;
Review ;
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the neck.
- Whiplash injury or other cervical spine trauma.
- Spinal infections.
- Spinal tumors and cancers
- Spondylosis
- Spinal cord compression or squeezed.
4)ans ; localization of spinal cord lesions
Plegia ;severe or complete weakness
Paresis : mild or moderate weakness
Monoplegia ; weakness of one limb
Paraplegia ; weakness of both lower limbs
Quadriplegia ; weakness of all 4 limbs
Diplegia ; quadriplegia in which lower limbs are affected more than upper limbs
Cord lesion above D12 segment
Acute state retention
Reflex bladder
Reflex emptying,vague sensation,small bladder
Conus lesion(
S3-CO1)
Autonomic bladder;
No bladder sensation ,dribbling, more residual urine
Cauda equina lesion (L2-co1)
Bladder sensation normal
Results of spinal cord lesion ;
At the level;
Motor; segmental LMN findings
Sensory ; segmental sensory root findings
Below the level
Motor :UMN findings
Sensory : tract involvement findings
Autonomic ; bowel.bladder
Others
Localization of C5 segment lesion
1)atC-5
a) motor LMN weakness of C5 myotome-deltoid and biceps
b) reflex; absent
c)sensory; radicular symptoms atC5
2) below C5
a) UMN findings
b) posterior column and spinothalamic tract involvement
Localization at D10 segment
Weaknesses of lower abdominal muscles
Absent lower abdominal reflex
Sensory dermatomal signs at D10
2) Below D10
a) UMN findings
b) posterior column and spinothalamic tract involvement


















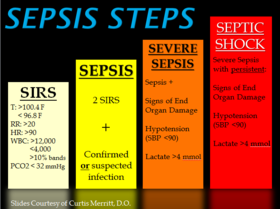
Comments
Post a Comment